Tooth Discolouration Causes and Treatment Options
Importance of a Healthy and Confident Smile
A healthy, confident smile shows beauty and reflects overall well-being. An attractive smile can boost self-esteem, improve communication, and lead to professional success, Brisbane cosmetic dentists say.
However, discoloured teeth can diminish a vibrant smile, causing self-consciousness. Understanding tooth discolouration causes and treatments can reclaim your confidence and let your smile shine, leaving a lasting impression on those around you. Read about teeth whitening in Brisbane.
Causes of Tooth Discoloration
Tooth stains vary in origin, type, and severity and can be classified into two main categories: extrinsic and intrinsic teeth discolouration.
Why do I have one discoloured tooth?
A single discoloured tooth can be concerning, and several factors could be contributing to this issue.
Trauma: If the tooth has experienced trauma, such as a knock or a fall, it can lead to internal bleeding within the tooth, causing discolouration. This is often a darkening or greyish hue.
Dental Procedures: Previous dental work, like a filling or root canal, can sometimes cause a tooth to change colour. Over time, materials used in these procedures may lead to a darker appearance.
Decay: Tooth decay can cause discolouration. As the structure of the tooth breaks down, it may appear yellow, brown, or black.
Dental Hygiene Habits: Poor oral hygiene can lead to plaque and tartar build-up, which might not affect all teeth uniformly. This could cause discolouration in specific teeth.
Dietary Habits: While dietary habits typically affect all teeth, in some cases, a single tooth might be more exposed to staining agents due to its position or condition.
Age-Related Changes: Generally, age affects all teeth, but if one tooth has worn enamel more than others, it might appear different in colour.
Symptoms to Watch For: If the discolouration is accompanied by pain, sensitivity, swelling, or changes in gum health around the tooth, it’s essential to seek emergency dental advice. These could be signs of decay, infection, or other dental health issues.
A dental examination is the best course of action to determine the specific cause and appropriate treatment for your discoloured tooth. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene, and a balanced diet can help prevent further discolouration and maintain overall oral health.
How can I stop my teeth from discolouration?
Preventing tooth discolouration involves a blend of good oral hygiene, mindful dietary habits, and professional dental care. Here are some effective strategies:
Oral Hygiene Routine: Consistent and proper oral hygiene is crucial. Brushing twice a day, using fluoride toothpaste, and flossing daily help remove plaque and surface stains. An Australian might consider using a toothbrush with soft bristles to avoid enamel erosion, which is more prevalent due to the Aussie lifestyle and diet.
Dietary Habits: In terms of diet, it’s wise to limit foods and drinks that stain teeth. This includes common favourites like beetroot, Vegemite, coffee, tea, and red wine. If you consume these, rinsing your mouth with water afterwards can reduce their staining effect.
Quitting Smoking: Tobacco, whether smoking or chewing, significantly contributes to tooth discolouration. Quitting these habits is beneficial for both oral and overall health.
Regular Dental Visits: Regular dental check-ups and cleanings with a Brisbane dentist or oral health therapist are vital. They can provide professional cleaning to remove surface stains and offer advice tailored to your specific needs.
Professional Whitening Treatments: For deeper stains, professional whitening treatments available in Australia, such as bleaching, can be more effective than over-the-counter products. These should be done under the guidance of a dental professional.
Avoiding Excessive Fluoride: While fluoride is essential for tooth health, too much, particularly during teeth development, can cause fluorosis, leading to discolouration. It’s important to use fluoride products appropriately.
Using Straws: For beverages like soft drinks, coffee, or tea, using a straw can minimise direct contact with your teeth, reducing the risk of staining.
Remember, each person’s teeth react differently to various substances, and what works for one person may not work for another. It’s always best to consult a dental professional to develop a personalised plan that suits your lifestyle and oral health needs in Brisbane.
Can a Discoloured tooth be fixed?
Treating or restoring a discoloured tooth depends on the cause of the discolouration. Here’s a straightforward guide to understanding the treatments and their effectiveness, considering various causes:
Surface Stains (Extrinsic Discolouration): Caused by foods, drinks, or smoking, these stains affect the outer layer of the tooth.
- Professional Cleaning: Regular dental cleanings can remove surface stains. In Brisbane, dental hygienists and oral health therapists often use specialised tools for this.
- Whitening Toothpaste: These can be effective for mild staining, but don’t expect dramatic changes.
- Professional Whitening Treatments: Bleaching procedures performed by dentists are more effective for these types of stains. However, they can cause temporary tooth sensitivity.
Internal Stains (Intrinsic Discolouration): Caused by medication, trauma, decay, or certain medical treatments.
- Internal Bleaching: A dentist might recommend internal bleaching for teeth discoloured due to internal factors. This is where the bleach is placed inside the tooth, particularly effective if the discolouration is due to root canal issues.
- Veneers or Crowns: If the discolouration is severe, dental veneers or dental crowns can be an option. These cover the tooth, providing a new, stain-free surface. However, they require altering the natural tooth structure, which is irreversible.
Age-Related Discolouration:
- Combination Treatments: Often, external and internal treatments are used. For example, a dentist in Brisbane might recommend professional Zoom teeth whitening followed by veneers if necessary.
Limitations and Risks:
- Tooth Sensitivity: A common side effect of bleaching treatments is increased tooth sensitivity, usually temporary.
- Damage to Tooth Enamel: Overuse of whitening products can damage tooth enamel, especially those bought over the counter without professional guidance.
- Gum Irritation: Some people experience gum irritation from bleaching products.
It’s important to consult a dentist to determine the most suitable treatment for your situation. They can provide advice tailored to your needs and the type of discolouration you’re experiencing, ensuring you understand each treatment option’s potential risks and benefits. Remember, what works for one person might not be suitable for another, so personalised advice is key.
What deficiency causes teeth discoloration?
Nutritional Deficiencies and Tooth Discolouration:
- Calcium Deficiency: This is a biggie. Teeth, like bones, need calcium. Not enough calcium can lead to weaker enamel, making teeth more prone to discolouration.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Vitamin D helps in calcium absorption. Low levels can indirectly affect tooth health and lead to discolouration.
- Iron Deficiency: Too little iron can lead to pale gums, making your teeth look more yellow in contrast. But too much iron can actually cause teeth to go a bit grey.
Now, let’s talk about non-dietary factors:
- Oral Hygiene: If you’re not brushing and flossing regularly, plaque and tartar can build up, leading to a yellowish tint.
- Medications: Some meds, especially certain antibiotics, can discolour teeth.
- Genetics: Just like eye colour, the natural colour of your teeth can be inherited.
- Ageing: Over time, the outer layer of your teeth wears down, revealing the naturally yellower dentine.
- Environmental Factors: Excessive fluoride (from water or products) can cause white spots or streaks on teeth, a condition known as fluorosis.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking or chewing tobacco and drinks like coffee, tea, and red wine can lead to external staining.
In summary, diet and lifestyle play a role in the health and appearance of your teeth. A balanced diet with sufficient calcium, vitamin D, and iron is important for dental health. Combined with good oral hygiene and mindful lifestyle choices, you can help prevent tooth discolouration. Remember, if you’re seeing significant changes in your tooth colour, it’s a good idea to consult your dentist or oral health therapist in Brisbane.
Extrinsic Tooth Staining
Extrinsic stains are surface stains that affect the outer layer, or enamel, of an adult tooth. These stains cause teeth discolouration, resulting from lifestyle habits such as consuming certain foods and drinks or using tobacco.
Teeth discolouration from extrinsic stains can stain your teeth and alter their appearance.

Food and Beverages
Consuming dark-coloured foods and beverages can cause tooth discolouration. Common culprits include coffee, tea, red wine, cola, and dark fruits and vegetables like berries, blueberries, blackberries, and cherries. These substances contain pigments that can adhere to the tooth enamel and cause dark spots on the teeth.
Tobacco Use
Smoking or chewing tobacco is another significant contributor that can stain teeth over time and compromise the natural tooth colour. Nicotine, a substance found in tobacco, can cause yellowish stains on the tooth surface, while tar, a dark, sticky byproduct of tobacco, can create brownish or black discolouration.
Poor Dental Hygiene
Intrinsic discolouration refers to the staining or darkening of teeth within the tooth structure. Unlike extrinsic discolouration, which affects the outer surface of the teeth (the enamel), intrinsic discolouration occurs in the dentin layer beneath the enamel.
Intrinsic Stains
Intrinsic discolouration refers to the staining or darkening of teeth within the tooth structure. Unlike extrinsic discolouration, which affects the outer surface of the teeth (the enamel), intrinsic discolouration occurs in the dentin layer beneath the enamel.
- Fluoride Exposure: Too much fluoride exposure can lead to fluorosis, which results in teeth staining. This type of tooth staining is due to intrinsic factors, as excess fluoride can disturb enamel formation during enamel development.
- Tetracycline Antibiotics: Antibiotics tetracycline can cause tooth discolouration if taken during enamel development, especially in children with developing adult teeth. Antipsychotic drugs may also cause tooth discolouration.
- Trauma or Injuries To The Teeth: Trauma or injury to adult teeth may cause teeth stains due to damage to the blood vessels, internal bleeding, or a dying nerve. The released blood components and byproducts can discolour the dentin, the inner layer of the tooth, resulting in a darker or yellowish appearance.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals are predisposed to teeth discolouration or stained teeth due to hereditary factors. These genetic factors can influence tooth enamel’s thickness, translucency, or mineral composition, leading to teeth naturally appearing more discoloured or prone to staining.
- Aging: Age-related tooth discolouration occurs as the tooth enamel wears down over time. This process exposes the yellow dentin layer, resulting in discoloured or stained teeth. As we age, the enamel becomes more prone to staining from external factors, further contributing to teeth discolouration.
- Dental Materials: Certain dental materials, such as amalgam restorations, can cause teeth to have a grey-black cast. Amalgam restorations are often made of silver sulphide-containing materials, which can corrode or tarnish over time. This corrosion can lead to discolouration of the surrounding tooth structure, resulting in a grey-black appearance on the affected teeth.
Intrinsic stains are more challenging to remove than extrinsic dental stains, which are on the tooth surface and may require professional dental treatment.
How To Prevent Tooth Discoloration
Practising good oral hygiene and following these guidelines can help prevent staining and maintain a bright smile.
- Regularly Brush and Floss: Brush your teeth at least twice a day for two minutes each time, and floss daily, as the American Dental Association recommends. Brushing and flossing regularly removes plaque and food particles that can cause staining, dental caries, and tooth decay.
- Rinse Your Mouths: After consuming stain-causing beverages or foods, rinse your mouth with water to help prevent staining. Using mouth rinses with fluoride can also help protect teeth from decay.
- Avoid Excessive Fluoride: While fluoride is essential for preventing tooth decay, too much can cause discolouration. Use fluoride-containing products in moderation and follow your dentist’s recommendations.
- Limit Stain-Causing Foods and Beverages: Coffee, tea, red wine, soy sauce and dark-coloured sodas can stain teeth. Consume them in moderation and use a straw when possible to limit contact with teeth.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups. Dentists can remove surface stains and monitor oral health to prevent tooth discolouration and other dental issues. The Australian Dental Association (ADA) recommends that people visit their dentist for a checkup and cleaning at least once every six months.
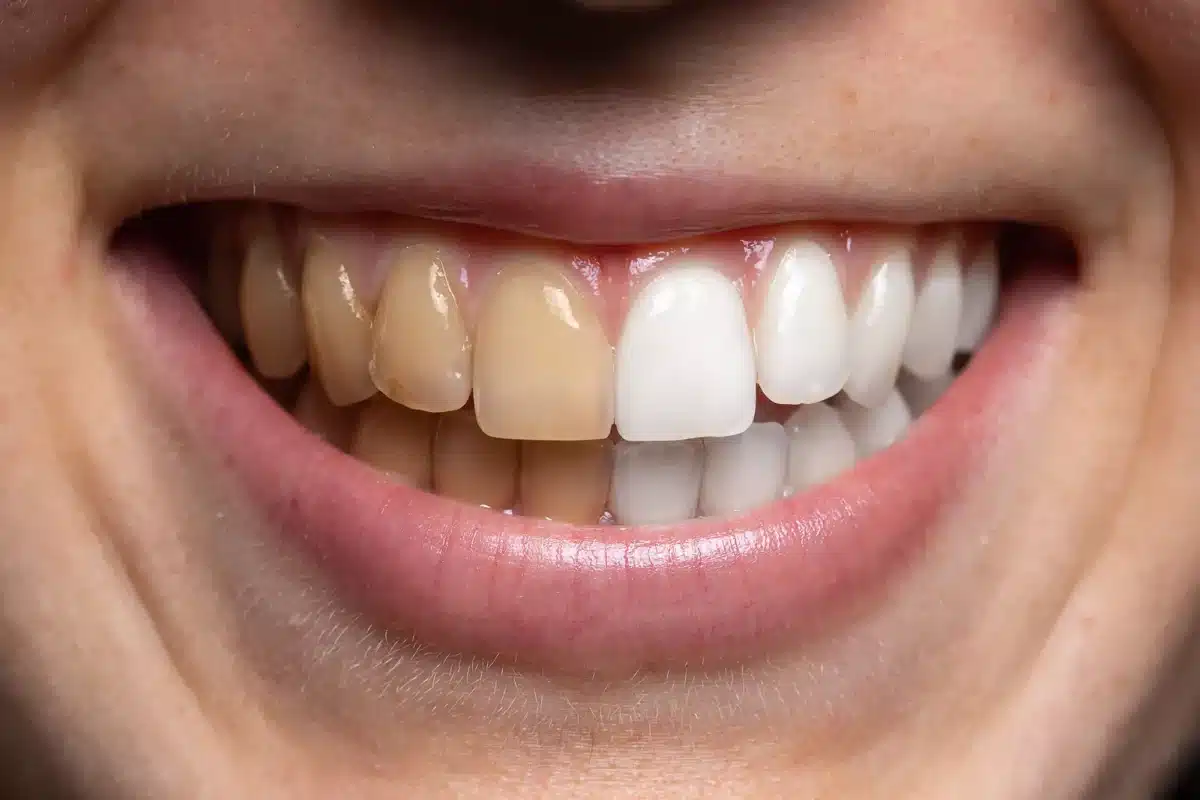
Treatment Options for Tooth Discolouration
Identifying the underlying cause is essential for selecting the most effective treatment and preventing further discolouration.
Treatment options for tooth discolouration include teeth whitening methods to whiten teeth and improve dental hygiene.
Whitening Toothpaste
Whitening toothpastes are a popular over-the-counter treatment option for mild tooth discolouration. To remove surface stains, whitening toothpastes typically contain mild abrasives like silica or calcium carbonate. Some also have chemical agents like hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide that break down stains to make them easier to remove.
While they can address extrinsic dental stains caused by smoking, coffee, tea, or red wine, they are not as effective for treating intrinsic stains or severe tooth discolouration.
Professional Teeth Whitening
Here’s an overview of the in-office tooth whitening procedure:
Professional teeth whitening is a cosmetic dental procedure that removes stains and discolouration from the teeth, resulting in a brighter and more appealing smile. The procedure is usually performed by a dentist or a trained dental hygienist and tends to be more effective and faster than at-home whitening methods.
- Initial Consultation: Before the procedure, you’ll have a consultation with your dentist to assess the current condition of your teeth, discuss your expectations, and determine if you’re a suitable candidate for the treatment. Your dentist may take photographs of your teeth to track progress and compare results.
- Dental Cleaning: Before the whitening procedure, your dentist will clean your teeth to remove any plaque or tartar buildup, which could interfere with the whitening process.
- Protection of Gums and Soft Tissues: Your dentist will apply a protective gel or rubber dam around your teeth to protect your gums and other soft tissues from the whitening agent. This step ensures that the whitening solution only comes in contact with your teeth, not the surrounding tissues.
- Application of Whitening Agent: The whitening solution, which usually contains hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide as the active ingredient, is then applied to the surface of your teeth. The concentration of the whitening agent used in in-office procedures is typically higher than in at-home treatments, making the process more effective and efficient.
- Activation of The Whitening Agent: Depending on the whitening system used, your dentist may use a special light or laser to activate the whitening agent. This step accelerates the breakdown of the peroxide, allowing it to penetrate the tooth enamel and break up the stains more effectively.
- Waiting Period: The whitening agent is left on your teeth for a predetermined period, usually 15 to 30 minutes. The process may be repeated in multiple sessions, depending on the desired level of whitening and the specific treatment protocol.
- Rinsing and Removal of Protective Barriers: Once the whitening process is complete, your dentist will rinse your mouth and remove any protective barriers applied earlier.
- Post-Whitening Care: Your dentist will provide instructions for post-whitening care, which may include avoiding certain foods and drinks that could stain your teeth and maintaining proper oral hygiene.
Keep in mind that individual experiences and results may vary, and not everyone is a suitable candidate for in-office teeth whitening. Consult with your dentist to determine the best option for you.
Take-Home Whitening Kits
Take-home whitening kits are another option to treat tooth discolouration. These over-the-counter products include whitening trays, strips, and gels that contain a lower concentration of a bleaching agent than professional treatments.
The kits allow users to whiten their teeth in the comfort of their own homes but may take longer to achieve desired results compared to in-office procedures.
Dental Bonding
Dental bonding, also known as composite bonding, is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the application of a tooth-coloured composite resin material to the surface of discoloured teeth.
It is a relatively quick and cost-effective solution for minor discolouration and other issues like chipped or cracked teeth, gaps between teeth, or minor shape irregularities.
Porcelain Veneers
Porcelain veneers are thin shells of dental-grade porcelain that are custom-made to fit over the front surfaces of your teeth. Dental veneers can correct cosmetic dental issues, including moderate to severe tooth discolouration and chipped, cracked, or misaligned teeth.

FAQs
In some cases, after RCT, the tooth may become darker over time.
Braces may cause tooth stains if proper oral hygiene is not maintained during orthodontic treatment. The stains can occur around the brackets and wires, making it challenging to clean teeth effectively. To prevent stains, maintain good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups.
At-home teeth whitening can pose risks such as tooth sensitivity, gum irritation, uneven whitening, and enamel damage due to overuse or misuse. To minimize risks, follow the product instructions carefully and consult a dentist before beginning any at-home whitening treatment.
Whitening teeth with baking soda is generally considered safe when used occasionally and in moderation.





































